Linux Mint 17 Virtualenv Python 2
How to Install and Getting Started with Python 2.X Virtualenv on Linux Mint 17 LTS GNU/Linux – Step by step Tutorial.
And a Virtualenv on Linux Mint 17 Environment, put simply, is an isolated working copy of Python which allows you to work on a specific project without worry of affecting other projects.
Finally, the Virtualenvwrapper include wrappers for creating and deleting virtual environments and otherwise managing your development workflow, making it easier to work on more than one project at a time without introducing conflicts in their dependencies.

-
Open a Shell Terminal emulator window
(Press “Enter” to Execute Commands)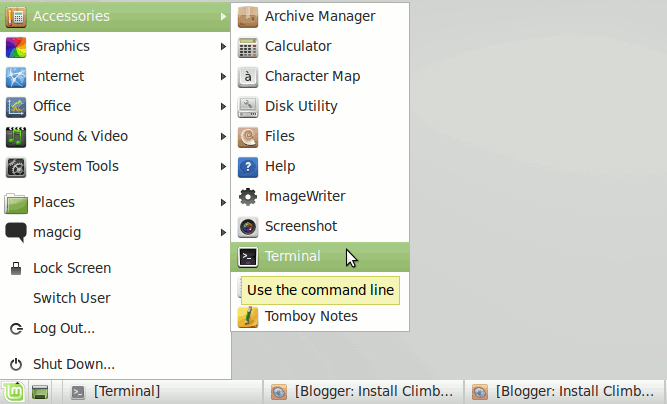
In case first see: Terminal QuickStart Guide.
-
Installing Virtualenv+Virtualenvwrapper.
sudo su -c "apt-get install virtualenvwrapper"
-
To Make a Python Virtual Environmnet.
mkvirtualenv test
-
To List All the Existing Virtual Environments.
ls $WORKON_HOME
-
To Switch the Virtual Environmnet.
mkvirtualenv essai
workon test
Show the Working Virtual Env:
echo $VIRTUAL_ENV
-
To Install Software into the Virtual Environmnet.
For Example:
pip install django
-
To List All the Virtual Environmnet Packages.
lssitepackages
-
To Automatically Run a Command after Environment Creation.
echo '[bash-command]' > $WORKON_HOME/postactivate
For Instance to Automatically Change to the New Env Directory:
echo 'cd $VIRTUAL_ENV' > $WORKON_HOME/postactivate
-
To Automatically Installing Commonly Used Tools.
echo 'pip install [myGoodTool]' > $WORKON_HOME/postmkvirtualenv
For Example:
echo 'pip install sphinx' > $WORKON_HOME/postmkvirtualenv
How to Install Google-Chrome Web Browser on Ubuntu
Install Aptana Studio for Html5, Javascript, CSS & Python
Getting Started with Python Selenium Testing Browser Environment: