Linux Mint Setting Permissions on File System
[ad_slider autoplay=”true” interval=”8″ count=”5″]
How to Set or Change the File/Directory Permissions on Linux Mint 17 Qiana Mate/Cinnamon/KDE/Xfce desktops.
To Follow the Tutorial you will Need to have a Little Practice to Work on the Mint Linux Console Terminal Command Line.
Included in the Article Links to Guides on Getting Started with Command Line on Linux Mint and to Setting Ownership over Linux Mint File System.

-
First, Open a Command Line Terminal Console Window
(Press “Enter” to Execute Commands)Mate:
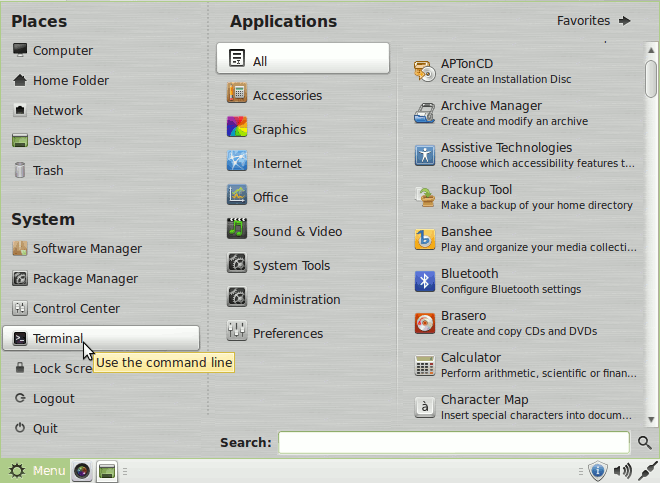
Cinnamon:
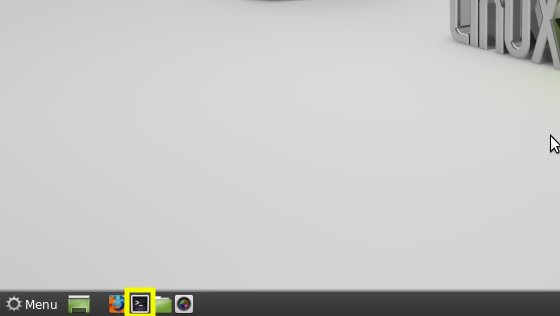
KDE:
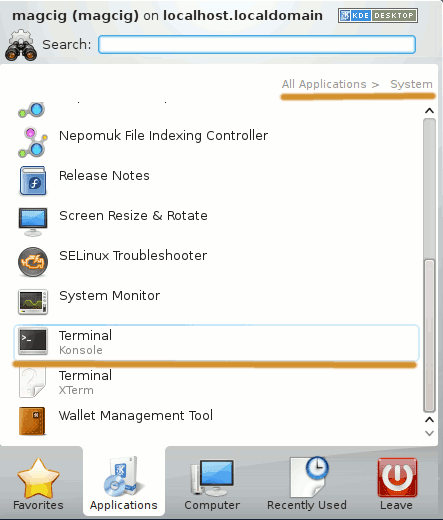
Xfce:
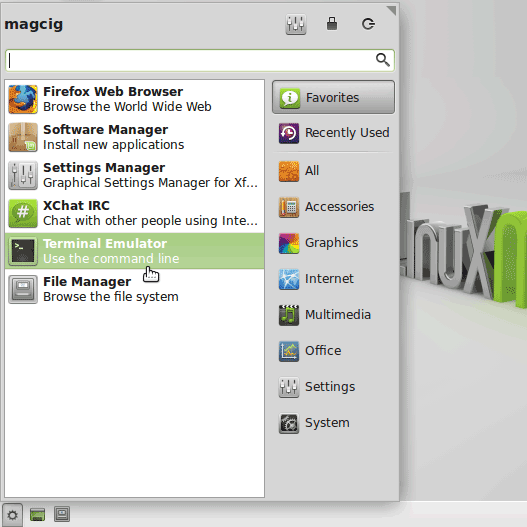
In case first see: Terminal Quick Start Guide.
-
Who Can Change File’s Permissions?.
- You Can Freely Change Permissions over Files/Directories Your User’s Hold.
- But you need Admin Super User Powers to Change Permissions on Entities he Do Not Hold!
-
Setting Up Permissions on Files and Directories.
- Use ‘u‘ to Setup Permissions for the User Owner
- Use ‘g‘ to Setup Permissions for the Group Owner
- Use ‘u+g‘ to Setup Permissions for the User and Group Owner
- Use ‘a‘ to Setup Permissions for All (World)
- Use ‘o‘ for Revoking Actual Permissions and Giving Permissions to the Others (the Before Disabled ones)
- Use ‘x‘ to Setup Execution Permission
- Use ‘w‘ to Setup Write/Delete Permission
- Use ‘r‘ to Setup Read Permission
- Use ‘+‘ to Give Permission
- Use ‘–‘ to Remove Permission
Basic Building Blocks for the Permission Command.
Ownership Types:
Permission Types:
Giving/Removing Permissions:
Generic Permission Command Form:
chmod ownershipSubject[+/-]r/w/x [myEntity]
For Instance :
mkdir $HOME/world
To Give ‘All’ (read,write/delete,execute) Permissions on the ‘world’ Directory to ‘Everybody’:
chmod a+rwx $HOME/world
(Normally Take Care Before to Open a Directory to the World Because this Can Compromise your System Security!)
Now to Check Permissions Setup:ls -l $HOME
To Remove the ‘Write/Delete’ Permission to the ‘World’:
chmod a-w $HOME/world
To Give the ‘Write/Delete’ Permission the ‘world’ Only to the Owner:
chmod u+w $HOME/world
To Give the ‘Write/Delete’ Permission the ‘world’ Also to the Owner’s Group:
chmod g+w $HOME/world
To Remove the ‘Execution’ Permission to the ‘World’:
chmod a-x $HOME/world
To Give the ‘Execution’ Permission to the ‘world’ to the Owner:
chmod u+x $HOME/world
To Give the ‘Execution’ Permission to the ‘world’ Also to the Owner’s Group:
chmod g+x $HOME/world
(After Only you and your Group will be able to Access the ‘world’ Directory Directory on Shell!)
-
How to Set Ownership on Linux Mint File System
Mint Setting Ownership Quick Start[ad_slider autoplay=”true” interval=”8″ count=”5″]
How to Quick Start with Command Line on Mint Linux